Introduction: In the realm of modern communication, the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) stands as a cornerstone, facilitating the seamless exchange of voice, video, and messaging across various devices and networks. As technology continues to evolve, SIP remains at the forefront, powering innovations like SIP trunking to streamline communication processes. This article delves into the intricacies of SIP, its significance in contemporary communication, and the emergence of SIP trunking as a game-changer in the telecommunications industry.
- What is SIP? SIP, or Session Initiation Protocol, is a signaling protocol widely used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating real-time communication sessions over IP networks. Originally standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in RFC 3261, SIP enables diverse communication applications such as voice and video calls, instant messaging, and multimedia conferencing.
- How SIP Works: SIP operates on a client-server model, where user agents initiate sessions by sending SIP requests to servers. These requests include INVITE (to initiate a session), REGISTER (to register the user’s location), ACK (to confirm session establishment), and BYE (to terminate a session). SIP servers, including proxy servers, redirect servers, and registrar servers, facilitate the routing and management of communication sessions.
- Significance of SIP in Modern Communication: SIP has revolutionized communication by providing a standardized protocol for interoperability among diverse devices and networks. Its flexibility and extensibility allow for seamless integration with other protocols and services, fostering innovation in unified communications, Voice over IP (VoIP), and WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) applications.
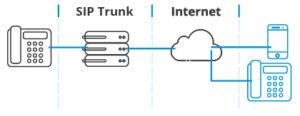
- Evolution of SIP Trunking: SIP trunking represents a significant advancement in telecommunications, replacing traditional analog or digital telephone lines with SIP-based connections over the Internet. This technology enables businesses to consolidate voice and data traffic onto a single IP network, leading to cost savings, scalability, and enhanced communication capabilities.
- Benefits of SIP Trunking:
- Cost Efficiency: SIP trunking eliminates the need for separate voice and data circuits, reducing telecommunications expenses associated with hardware, maintenance, and long-distance calling.
- Scalability: SIP trunks can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate changing business needs, allowing organizations to pay for only the channels and capacity they require.
- Flexibility: With SIP trunking, businesses can support a variety of communication methods, including voice, video, and messaging, while integrating with existing PBX systems and communication applications.
- Disaster Recovery: SIP trunking offers built-in redundancy and failover options, ensuring business continuity in the event of network outages or disasters.
- Implementation Considerations: When adopting SIP trunking, organizations must consider factors such as network infrastructure, bandwidth requirements, security measures, and Quality of Service (QoS) considerations to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
- Future Trends in SIP and SIP Trunking: The future of SIP and SIP trunking holds promise for further innovation and integration with emerging technologies such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence. These advancements will continue to drive efficiency, connectivity, and collaboration in the digital age.
Conclusion: As the protocol driving modern communication, SIP plays a pivotal role in enabling seamless, real-time interactions across global networks. With the advent of SIP trunking, businesses can leverage the power of SIP to enhance their communication infrastructure, reduce costs, and stay ahead in an increasingly interconnected world. By embracing SIP and its associated technologies, organizations can unlock new opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and growth in the ever-evolving landscape of telecommunications.